Do you experience pain while riding?
As avid cyclists ourselves, we know firsthand the toll that years of hard-earned riding can do to your back, your knees, your muscles, and your body in general. Nasty spills, the same positions, countless pedals, arduous climbs, burning lungs, and everything else that makes the challenges we face on the bike that much more rewarding…it all has a price.
We often come out on the other end with tight muscles, achy joints and chronic pain. This begs the question: “Is cycling itself the problem?”
Well, yes and no.
Yes, because there are components to the sport of cycling that encourage the development of overuse injuries. The fact that we remain stationary in a seated position while riding, that we are hunched over to reduce wind resistance, and that we tend to ride for hours at a time over incredibly long distances (to name a few).
No, because there are things we can do to prevent our bodies from breaking down so we can continue to enjoy and excel at the sport we love.
And it’s these preventative measures that inspired us to write a book…
Ride Pain Free: Stretching & Mobility Program for Cyclists
I Love Bicycling and Dynamic Cyclist joined forces to bring you this 7-day guided program that addresses the most common muscle imbalances for cyclists with both dynamic and static exercises. Each routine is designed for cyclists to target the common issues they endure by our team of physiotherapists, athletic therapists, and personal trainers. Through easy-to-follow routines, we will target all areas of the body, and teach you how to alleviate tension and improve posture for pain free riding!
Why We Wrote It
We wrote this book to address the unique needs of cyclist’s worldwide; to help them stay healthy and injury-free.
Cyclist’s face a number of challenges when it comes to injury prevention, and in few sports is it more important to find balance in the rest of your training. We understand how hopeless it can feel to be left with debilitating pain that keeps you off the bike, and we’re here to tell you that there is always a way to not just heal, but thrive.
Stretching and mobility are poorly understood concepts in most sports, and even more poorly practiced. By incorporating the correct stretches and mobility exercises into your routine, and giving yourself the time to open up and counteract the hours you spend on the bike, your body will be that much more prepared to tackle anything you throw at it, on or off the bike.
As cyclists, we understand the specific needs of our sport and the types of injuries we are all susceptible to on the bike. We felt we were well positioned to address those needs with a detailed, 7-day instructional program that is fun to do, easy to follow, and can be done in a condensed time period to accommodate any schedule.
We wanted to show people how easy it is to make a difference in your own body in just 15 minutes a day. And that’s exactly what we hope this book will do for you.
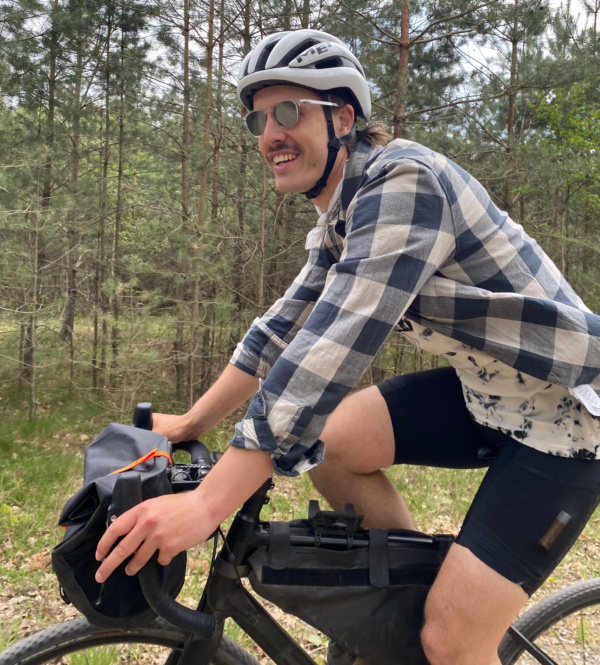
torwaiphoto/Adobe Stock
How This Book Can Help You
The fact cycling keeps a person in the same positions, doing the same things, repeatedly, is both a blessing and a curse.
The bad part about it is that, without properly implemented stretching and mobility protocols, we’re bound to develop overuse injuries that cause pain, dysfunction, and demotivation. The good part, though, is that we can tell where these problems are coming from, and systematically address them through our training.
Some of the common problems cyclist’s experience that we talk about in this book are:
- Low Back Pain
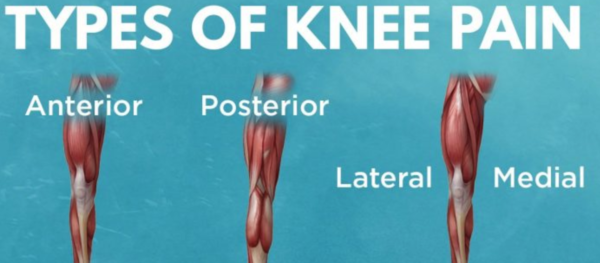
- Knee Pain
- Tight Hamstrings
- Neck Stiffness
You will learn about why these tend to develop over time as a result of cycling, the symptoms you may experience, and most importantly, what you can do to resolve the problem and get back to smooth, enjoyable riding!
While going through the routines, you’ll notice that each exercise has a supplementary benefits section that teaches you what it does for the body and why we’re including it. This helps the book to be not just a follow along workout regimen, but an educational resource that will help you train smarter and harder to become the best possible cyclist you can be.
Sidekick/Adobe Stock
Start Riding Pain Free TODAY
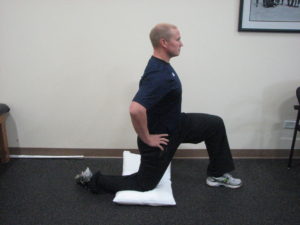
Sometimes a little guidance is all you need, and if you’ve been dealing with nagging pain, aching joints, and any other recurring problems on your cycling journey, this book was written for you. Accompanying the written directions are instructional photographs detailing the steps of each exercise, making it fun and easy to read through; it’s like having a workout partner right there with you at home!
Our team of dedicated health professionals and experienced cyclists want to help you enjoy the sport you love. Invest in your health and performance, and get your copy of Ride Pain Free: Stretching & Mobility Program for Cyclists today!



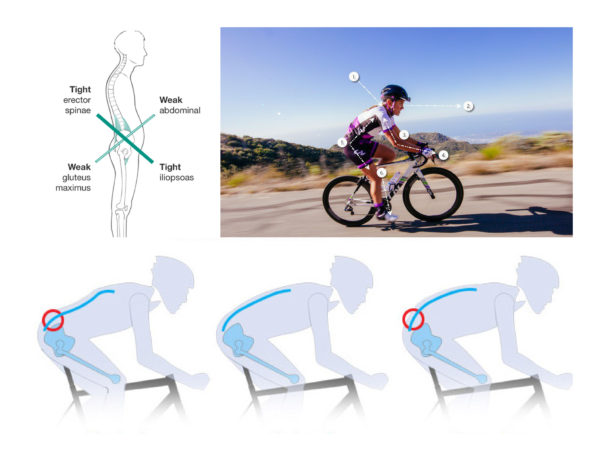
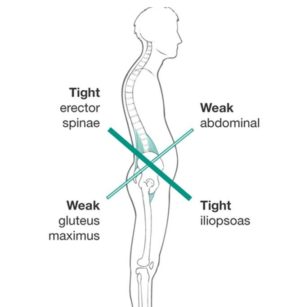
 if action is not taken. Not only will shortened muscles impact your efficiency, comfort, and aerodynamics on the bike, but they will eventually lead to injury.
if action is not taken. Not only will shortened muscles impact your efficiency, comfort, and aerodynamics on the bike, but they will eventually lead to injury.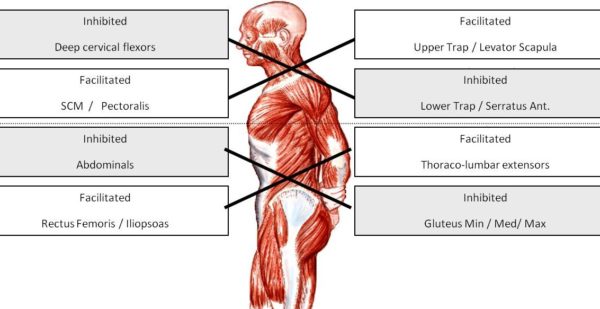
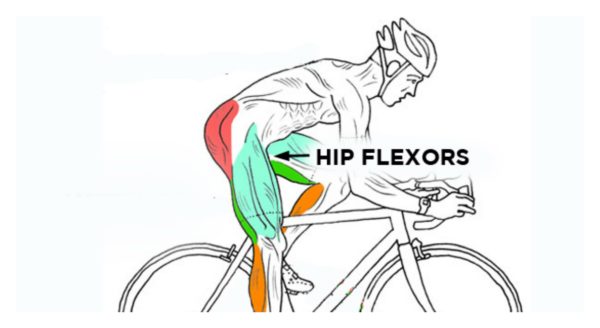
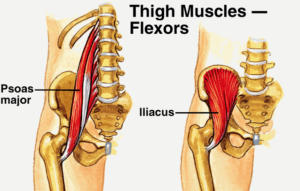
 abdominals and gluteals, are never fully engaged in cycling, while the facilitated muscles, rectus femoris (quadraceps), iliopsoas and thoraco-lumbar extensors are always engaged and often overworked. Constantly engaging those lower back muscles without proper support from a stable core often results in lower back pain for cyclists.
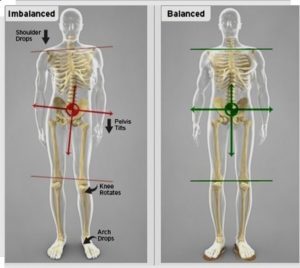
abdominals and gluteals, are never fully engaged in cycling, while the facilitated muscles, rectus femoris (quadraceps), iliopsoas and thoraco-lumbar extensors are always engaged and often overworked. Constantly engaging those lower back muscles without proper support from a stable core often results in lower back pain for cyclists.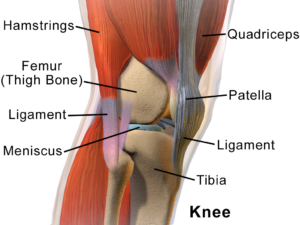 To make matters more complicated, the ITB runs down the outside of the thigh and blends into the outside of the knee. ITB stands for iliotibial band and is a well known potential source of trouble for cyclists, runners and active people in general. The ITB is also attached to your glutes (buttock muscles) and hip flexors. Often when looking for the source of knee pain we have to pay close attention to hip flexibility and control.
To make matters more complicated, the ITB runs down the outside of the thigh and blends into the outside of the knee. ITB stands for iliotibial band and is a well known potential source of trouble for cyclists, runners and active people in general. The ITB is also attached to your glutes (buttock muscles) and hip flexors. Often when looking for the source of knee pain we have to pay close attention to hip flexibility and control.
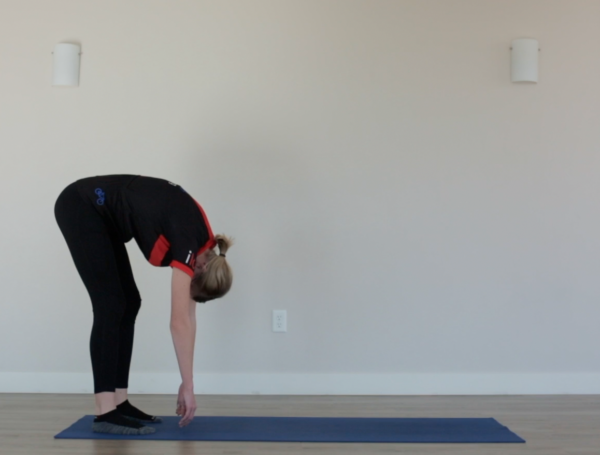
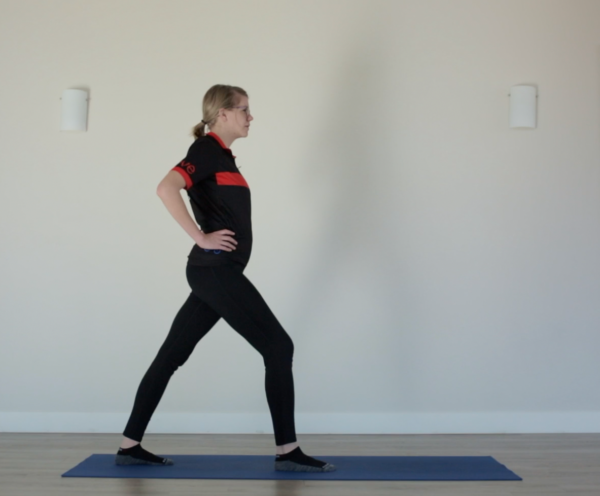
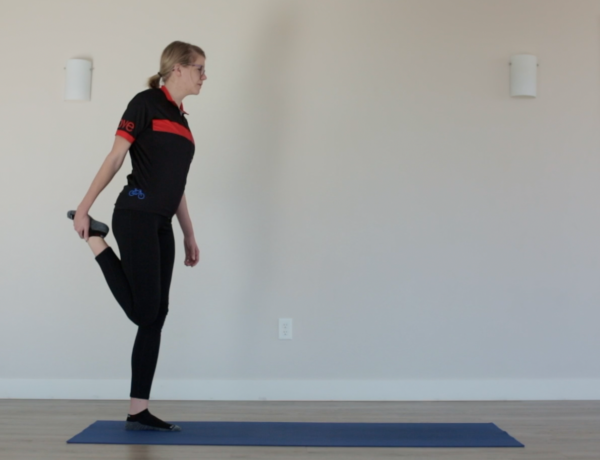















 Injury Prevention
Injury Prevention

